Obesity has become one of the most pressing health issues of our time, affecting millions of Americans and imposing a staggering economic burden on the healthcare system. This blog post explores the impact of obesity on individuals and society, delves into the underlying causes rooted in American culture, and examines the role of the food industry in perpetuating this epidemic.
The Impact of Obesity on Health and Healthcare Costs
Obesity significantly increases the risk of numerous health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Obesity is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess body weight is strongly linked to insulin resistance and the development of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Hypertension: Obesity often leads to high blood pressure, a key contributor to heart disease.
- Dyslipidemia: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are common in obese individuals.
- Sleep Apnea: Excess weight can cause breathing difficulties during sleep.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is prevalent among those with obesity.
- Certain Cancers: Obesity is associated with increased risk of several cancers, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
Severe joint pain and degeneration- This often leads to preventable and costly surgeries. - Chronic low-grade, systemic inflammation- Inflammatory cytokines lead to cell death and inflammation in adipose (fat) tissue, which causes spillover of insulin, toxic chemicals, and lipids. This inflammation can also degenerate nerve cells all over the body, including the brain, leading to increased risk of Parkinson’s and Dementia related disorders.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Obesity can lead to physical limitations, psychological issues, such as depression and anxiety, and a decreased overall quality of life.
The economic impact of obesity is equally alarming. The annual medical costs related to obesity in the United States are estimated to be in the billions, with individuals with obesity incurring significantly higher weight. These costs include direct medical expenses, such as doctor visits, medications, and surgeries, as well as indirect costs like lost productivity and absenteeism.
Cultural Factors and the Rise of Obesity
The prevalence of obesity in America is not merely a result of individual choices but is deeply intertwined with cultural and socioeconomic factors. Several aspects of American culture make it difficult to avoid developing diabetes and obesity:
- Dual-Income Households: The need for both parents to work full-time jobs leaves little time for meal preparation, making fast food and convenience foods an attractive option.
- Busy Lifestyles: The demands of work, homework, and extracurricular activities create a stressful environment where quick and easy food options are often the only feasible choice.
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Dual-income households, 40 hour work weeks, long commutes, office jobs, and busy lifestyles also make living an active lifestyle or finding the time and energy to exercise a very hard feat, as well. It can be done, but it’s not particularly easy and requires a lot of discipline.
- Economic Constraints: The rising cost of groceries can make it more affordable to eat fast food/processed/ pre-made foods than to cook three healthy meals a day.
The Toxic Food Environment
American food is often filled with chemicals, preservatives, unhealthy fats, and added sugars that contribute to insulin resistance and obesity. These ingredients not only undermine health but also create a cycle of addiction and overeating:
- Addictive Nature of Food: High-sugar and high-carb foods are designed to be addictive. They digest quickly, causing blood sugar spikes followed by crashes, which make people hungrier sooner and more likely to overeat.
- Chemical Additives: Many American food products contain ingredients that are banned in other countries due to their health risks. For example, artificial dyes, preservatives, and trans fats that are common in the U.S. are prohibited in many parts of Europe.
An example of a typical American meal that contains ingredients outlawed in other countries is a fast-food burger meal with soda and fries. This meal often includes: - Sodium Nitrite/Nitrate: Used in processed meats, banned in several countries due to cancer risk.
- Brominated Vegetable Oil (BVO): Found in sodas, banned in Europe and Japan due to potential reproductive and behavioral risks.
- Artificial Food Dyes (e.g., Red 40, Yellow 5, Blue 1): Linked to hyperactivity in children, immune disorders, and allergies. These are banned in the European Union.
- High-Fructose Corn Syrup: Common in sodas, boxed snacks, and desserts, associated with increased risk of obesity and diabetes.
- Azodicarbonamide: Used as a dough conditioner in burger buns, banned in Europe and Australia due to its link to respiratory issues and other health risks.
Rising Obesity Rates
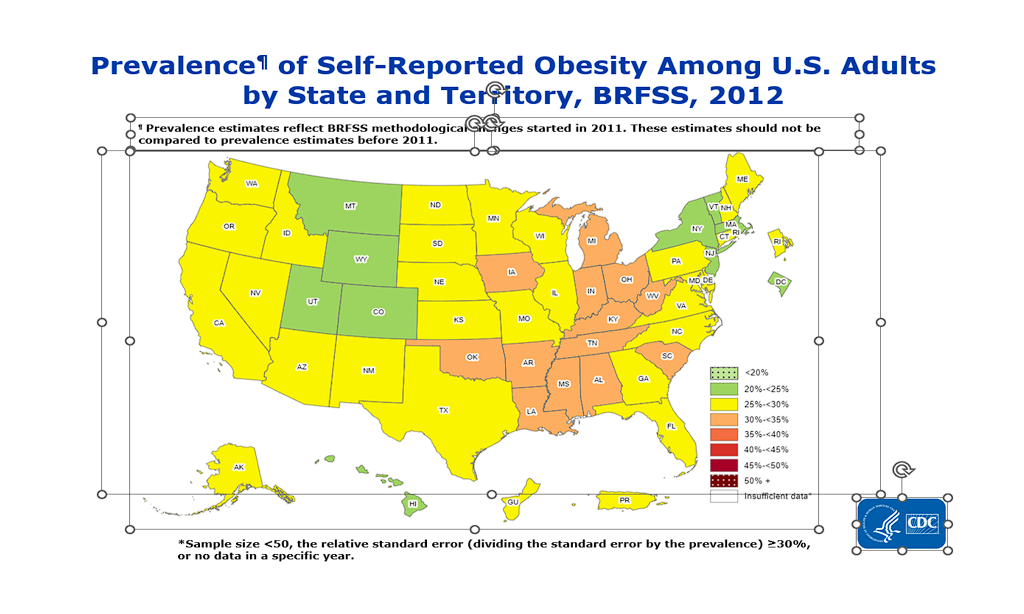
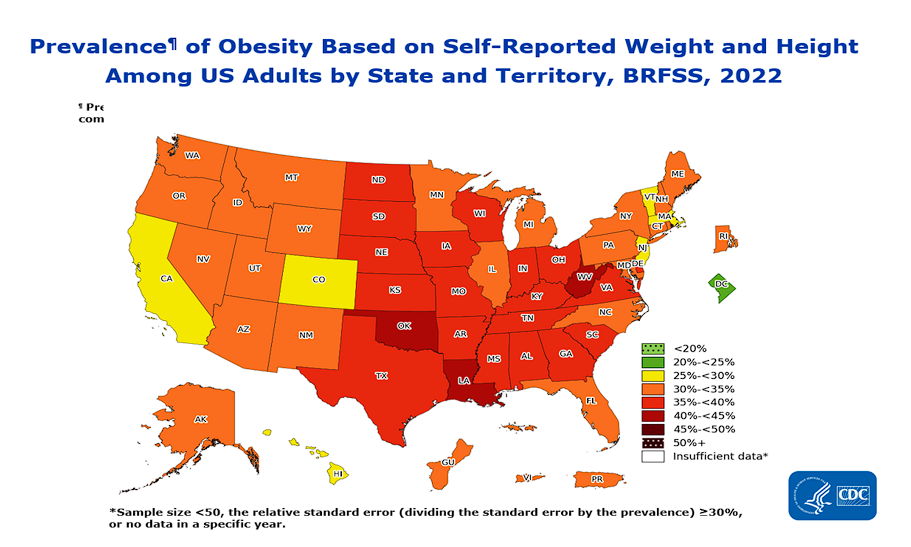
The rate of obesity in the United States has seen a significant incline over the past decade. From 2012 to 2024, the prevalence of obesity increased from 34.9% to 42% among adults. This sharp rise is a clear indication of the growing health crisis. According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of states with obesity rates of 35% or higher increased from 7 states in 2013 to 19 states in 2022. And this only includes the rates for the BMI’s that are considered obesity. This doesn’t include the rates for those with a BMI >26-29.9%, which is considered the “overweight” category. The prevalence of overweight adults is currently 30%. This means that over 70% of Americans are not in a healthy weight for their body habitus. Let me break that down in a simple way. For every 100 adults, 70 are overweight or obese. These numbers are staggering. Take a look at the chart below.
Studies and International Comparisons
A growing body of research highlights the detrimental effects of the typical American diet and the stark differences between food regulations in the U.S. and other countries. For instance:
• A study published in the Journal of Food Additives and Contaminants details how many additives allowed in the U.S. are banned elsewhere due to their adverse health effects.
• Research in The Lancet highlights the role of dietary patterns in the prevalence of obesity and related diseases.
• The New England Journal of Medicine discusses the global perspective on obesity and its associated risks.
Conclusion
The impact of obesity on health and healthcare costs is profound, and the cultural and environmental factors contributing to this epidemic are deeply embedded in American society. Addressing obesity requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy changes, public health initiatives, and individual efforts to make healthier choices despite the challenges. By understanding the root causes and making informed decisions, we can work towards a healthier future for all Americans.
As a healthcare provider, I will take a preventive approach to treating obesity and diabetes. I don’t wait until my patient’s A1C is >6.5% (or even >5.7%, for that matter) before I start treatment for diabetes or even tell them that they need to change their lifestyle first. We start BEFORE this occurs. I check a fasting insulin level, insulin sensitivity, and blood sugar and if it’s on the higher end of “normal” we start treatment immediately. In fact, I don’t work around “normal” levels at all. I aim for “optimal.” Why would you want to be normal, when normal is what it is today. Don’t wait until you are already overweight, obese, prediabetic, or insulin resistant to start taking your health seriously.
Insulin resistance can develop and linger for YEARS before it turns into diabetes. Which also means the complications that come with diabetes are developing slowly, but surely, before the numbers will show it. Your pancreatic beta cells are slowly dying off and your body’s ability to compensate/heal it is significantly reduced. Read this blog post (attach link to blog- Understanding Insulin Resistance: The Silent Precursor to Diabetes) about how insulin resistance can affect you and the steps you can take to mitigate or reverse it.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps.
Retrieved from Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps | Obesity | CDC
Gregg EW, Shaw JE. Global health effects of overweight and obesity. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377(1):80–1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1706095
Seifu CN, Fahey PP, Hailemariam TG, Frost SA, Atlantis E. Dietary patterns associated with obesity outcomes in adults: an umbrella review of systematic reviews. Public Health Nutrition. 2021;24(18):6390-6414. doi:10.1017/S1368980021000823
Simmons, A.L., Schlezinger, J.J. & Corkey, B.E. What Are We Putting in Our Food That Is Making Us Fat? Food Additives, Contaminants, and Other Putative Contributors to Obesity. Curr Obes Rep 3, 273–285 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-014-0094-y